Since it has been time to change for over five decades now how do we identify and deal with the obstacles to making a transition to an energy neutral and pollution free society?
Land use and land use change = LULUCF
Loss of reassuring places that nourish e-services and e-goods
Four Fs – are - food, fiber, fuel, forage
Four Fs refers to factual needs for natural sources of food, fuel, fiber & forage
1) food, all creatures require nourishment
2) fuel, all societies use dung, wood, water, oil, coal, gas, or sunlight for energy
3) fiber, especially for construction, but humans use clothing and paper
4) forage, bulky food such as grasses or hay for livestock, to gather.
The paradox of dominance is that the more dominant an animal we become the more vulnerable we are to damage and ecological degradation.
| Imperative means actions that must become behaviorally more common to prevent, loss, degradation, or irretrievable conditions. | ||
| Outline
|
||
 |
|
|
|
||
Scope: “The roots of
global change go far back in time . . . “
“When Scientists talk of global change today, they are usually referring to human-caused changes in the environment of sufficient magnitude eventually to reduce the capacity of much of the Earth to support organisms, especially Homo sapiens."
"This is a very recent development–a result of the rise of Homo sapiens to planetary dominance."
p. 235
"Land cover change was dramatic during the twentieth century and is still proceeding rapidly. More than seventy percent of the world's temperate broadleaf forests...had been chopped down by 1950."

Clear cutting an evergreen, coniferous forest in Oregon, 2009.
"Such land-cover disturbance is usually also accompanied by fragmentation of the remaining habitat."
p. 237.
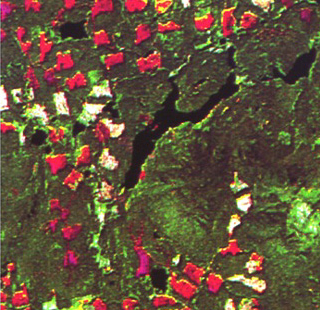 |
The red and pink areas are clear cut forest land in patches or fragments. |
|
|
An example of fragmented clear cut land from 1978-1980 in British Columbia, where more acres of forested land have been timbered than in the Amazon basin. |
|
"Nevertheless, many of the previous attributes of the forests will be restored if wildlife gradually returns. Not so in tree plantations, which are essentially monocultures and quite inhospitable to most wildlife and other plants."
p. 239.
"Land use changes can have dramatic impacts on aquatic systems as well."
p. 239.
Agriculture and Its Challenges
Agriculture and arable land are a significant portion of the terrain on earth.
We are an
"environment-dominating and environment-transforming animal."
"Now at least 20 percent of the ice free land surface is covered by crops, and more than another 25 percent is is devoted to grazing domestic animals."
p. 240.
The Earth's Oceans are the conveyors of essential materials in the planetary machine.
1). They are the heat engine of the planet driving winds, currents, and climate.
2). oceanic fisheries are a source of most or the earth's food and fertilizers.
Oceans: An Open Access Resource
The ultimate tragedy of the commons, oceans remind us that nature has the last word in the tragic dialogue that represents humans and the natural world.
"It's a process... 'fishing down the food web.' Daniel Pauly calls it..."
"many critical resources are 'open access' or nearly so. An open access resource is a service or good that no one owns–one over which nobody exercises property rights."
"Such resources ...are available for anyone and everyone to exploit, and the result is often is overexploitation or even the destruction of the resource."
"Economists call them ' common pool resources' when it is difficult or impossible for some actors to prevent other actors from exploiting them."
245.
Two capacities are basic to understanding how human civilizations miss the signals:
A] assimilative capacity – barely sensed
B] carrying capacity – crowded, overgrazed, overfishing -- the collapse of the Cod!
A= pollution and dead zones "calcite shells are threatened by acidification...."
B = "overharvesting" and "bottom trawling"
"This century is the last century of wild seafood."
p. 246.
Homogenization of nature
"All over the world, invasive species are causing problems for agriculture in particular and people in general."
Zebra mussels "starving native fish" of the Great Lakes.
• Lates niloticus deliberate sport fishery, introduction disrupted the diversity of cichlid natives
• Mayetiola destructor damages $1000 worth of wheat some years takes a decade to evolve resistance to wheat resistant strains.
• Boiga irregularis on Guam attached birds, mammals & people, snakes on a plane!
"Over much of the planet, exotic earthworms, spread by anglers and horticulturists, are battling with native ones, with variable and sometimes distressing results for local ecosystem services."
Toxic substances
"Ecologists also were initially quite slow to begin investigating human generated global change, including the distribution of toxic substances, and its consequences."
p. 250.
"Another trend that may be related to toxification is a worldwide decline in amphibians."
"Professor Tyrone Hayes of the University of California, Berkeley, has in fact produced persuasive evidence that the weed killer atrazine escaping from farm fields is involved in causing reproductive difficulties in leopard frogs."
p. 249.
"One of the most difficult to evaluate of all the global changes is the toxification of the planet."
"But the impact of global low-dose pollution of multiple substances on both human health and the health of ecosystems is more difficult to evaluate."
p. 248.
- bisphenol A, "present in the milk that mother's feed their babies...."
- DDT -- "much of the residues in a fish is added to . . . a seal."
- Atrazine -- a weed killer
- biomagnification, "residues...that easily dissolve in fat are not lost at high rates, as is useful energy, when they move up food chains Rather they concentrate; more and more poison is found in every step upward."
- mercury, "the open source" fingerprint contaminant [JVS]
pp. 248-249.
". . . our species would still be in trouble."
2002 study:
"This study, . . . estimated that humanity's 'load' was equal to about 70 percent of the biosphere's regenerative capacity in 1961, when the human population was about 3 billion and per capita (per person) consumption of resources and energy was far less than today's."
p. 251.
"that either human behavior toward the environment had to change or the number of people would have to be reduced...."
p. 251.
Tying it all together
"Those 850 million people in the world who are significantly undernourished and the 6 million children dying needlessly each year of malnutrition serve as a stark index of extreme poverty."
pp. 252-253.
"The various current trends that are generating global change and population overshoot (growth) are, as one might expect, not independent."
“It is commonplace to believe that hunger in the world is due to poverty and a malevolent economic system, but that population growth is not connected to the problem.”
p. 252.
“Certainly factors such as agricultural subsidies in rich countries and pressures to produce cash crops for export in poor countries have contributed considerably to problems of hunger and famine. So have the gross inequities in income and power that plague humanity.”
p. 252.
Summary
“Global change not only modifies the environment in which organisms are evolving genetically: it can have a major impact on our human cultural evolution as well.”
p. 254.
The human condition:
“Poverty is one of the worst environmental problems because it requires people wrest a living from their land without regard to the environmental consequences. It also deprives nearly a third of the global population of any power to improve the world their descendents will inhabit.”
253.
“Yet, if everyone were willing and able to share more equitably–for example if the rich were willing to modify their current diets, significantly reducing their consumption of beef and other animal products–then hunger might be largely eliminated, and as a bonus the flux of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere would be significantly reduced.”
p. 253.
“If the human population were not already huge and still growing, providing that basic diet would be much easier and would carry many fewer environmental risks.”
253